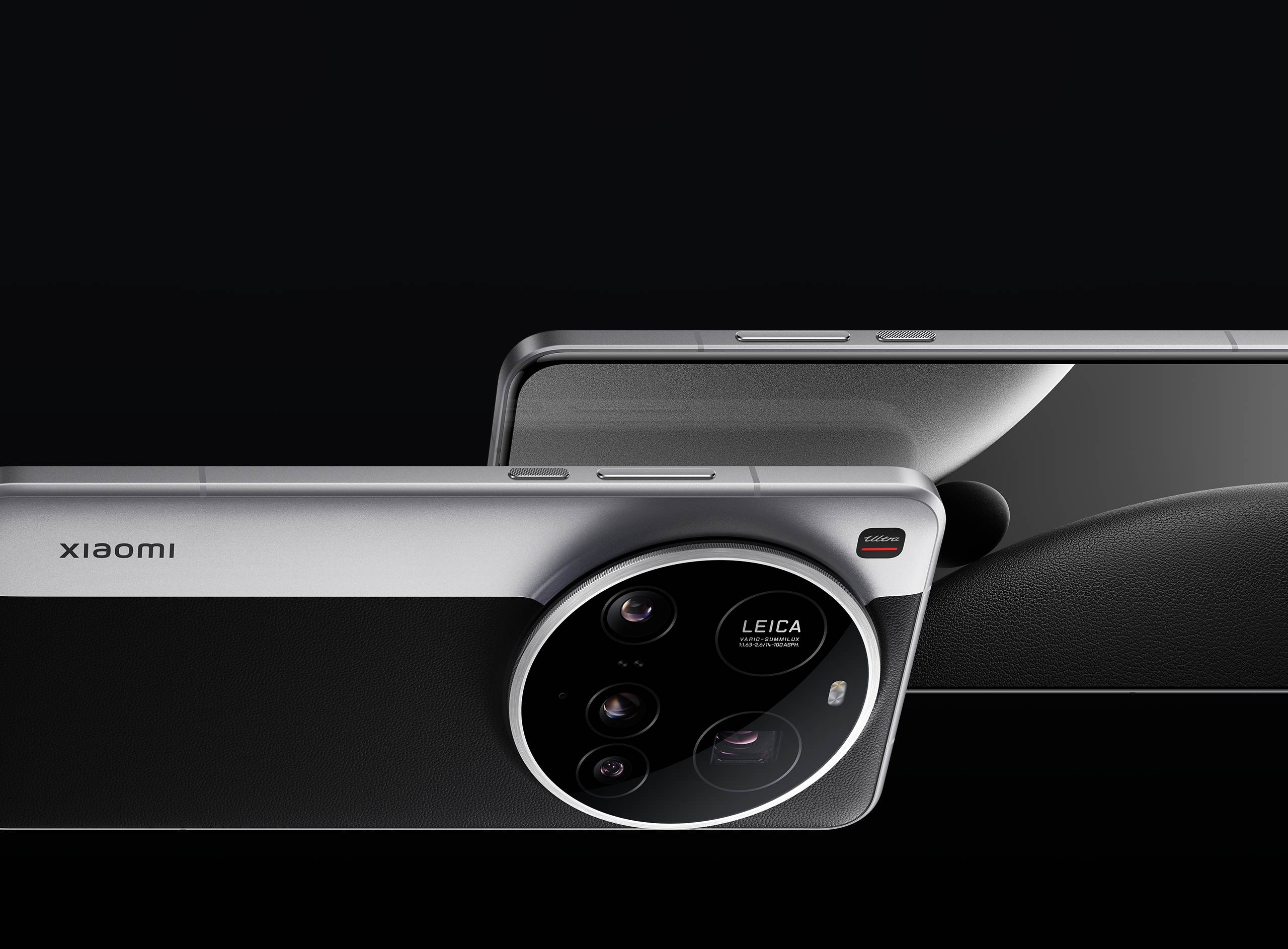
Featuring a high-end camera setup, cutting-edge Snapdragon 8 Elite processor, and a vivid 6.73-inch AMOLED display. In contrast, offering solid flagship specs with a slightly smaller AMOLED display and a large battery, all at a more affordable price point. Below is a tech vlogging-style breakdown, their specs, and how they stack up against each other—with a comparison chart included for quick visual reference.
- Display: 6.73-inch LTPO AMOLED, QHD+ (1440 x 3200), 120Hz refresh rate, 3200 nits peak brightness, Xiaomi Shield Glass 2.0 for enhanced durability.
- Processor: Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Elite (3nm), octa-core up to 4.32 GHz with Adreno 830 GPU.
- RAM & Storage: Options up to 16GB LPDDR5X RAM and 512GB/1TB UFS 4.1 storage; no card slot for expansion.
- Cameras (Rear): Quad camera setup:
- Front Camera: 32 MP punch-hole with 4K video support.
- Battery: 5410mAh (global), supporting 90W wired, 80W wireless, and 10W reverse wireless charging.
- Build & Durability: IP68 water and dust resistance; glass-fiber or eco-leather back; aerospace-grade glass fiber frame.
- Other Features: Ultrasonic in-display fingerprint sensor, full suite of sensors, IR blaster, Wi-Fi 7, Bluetooth 6.0, dual stereo speakers with Hi-Res audio.
- Software: Android 15 with Xiaomi HyperOS 2, promised 4 major updates.
- Price (India): ₹1,09,999 for 16GB/512GB; includes photography kit with pre-order in India.
OnePlus 13S: Complete Specifications
The OnePlus 13S offers a robust flagship experience, focusing on performance and battery endurance:
- Display: 6.32-inch LTPO AMOLED, 1216 x 2640 pixels (FHD+), 120Hz refresh rate, 1600 nits peak, Crystal Shield Glass protection.
- Processor: Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Elite (3nm), octa-core up to 4.32 GHz, Adreno 830 GPU.
- RAM & Storage: 12GB LPDDR5X RAM with 256GB/512GB UFS 4.0 storage; no microSD expansion.
- Cameras (Rear): Dual camera setup:
- Front Camera: 32 MP with 4K video.
- Battery: 5850mAh, 80W wired charging (with PPS/PD/QuickCharge support), 5W reverse wired.
- Build & Durability: Lighter at 185g, glass front, aluminum frame, IP65-rated (protection from dust/low-pressure water jets).
- Other Features: Optical in-display fingerprint, stereo speakers, Wi-Fi 7, Bluetooth 6.0.
- Software: Android 15 with OxygenOS 15.
- Price (India): ₹59,998 for 12GB/512GB.
Feature Comparison Chart
Below is a side-by-side comparison to highlight key areas:
Comparison chart of Xiaomi 15 Ultra vs OnePlus 13S major specifications, price, and launch details
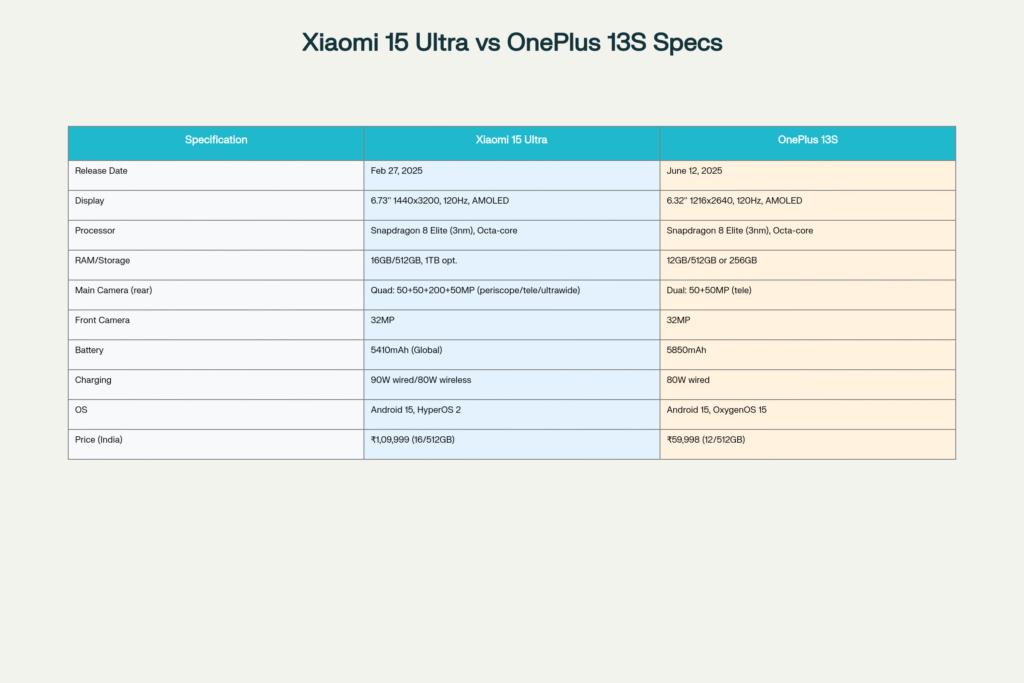
In-Depth Vlog-Style Breakdown
Display & Design
Both phones bring flagship displays but with distinct approaches. The Xiaomi 15 Ultra offers a larger, higher-res panel with extreme peak brightness suitable for HDR content and sunlight legibility, surrounded by premium glass and eco-leather or glass-fiber options—a treat for those who value both durability and aesthetics. OnePlus 13S, being smaller and lighter, feels more ergonomic, though its screen is slightly less dense and bright—still plenty sharp for everyday use.
Camera Prowess
Photography defines Xiaomi’s Ultra, with its Leica-engineered quad camera array rivaling professional shooting gear, especially the unique 200MP periscope telephoto for far-off zoom and the massive 1″ sensor for great low-light shots. It’s a phone for content creators craving versatility: 8K video, wide-to-ultra zoom, RAW, Pro Modes—delivering what few phones can. OnePlus 13S, while using high-quality sensors, sticks to a dual setup—a reliable performer for portraits and day-to-day, but doesn’t match Ultra’s zoom flexibility or creative features.
Performance & Software
Both are equipped with the Snapdragon 8 Elite, making them some of the fastest Androids in 2025. This processor, paired with UFS 4.1 (Ultra) or 4.0 (13S) storage, ensures smooth multi-tasking and gaming. The Xiaomi 15 Ultra boasts up to 16GB RAM, making it friendlier for heavy users who keep lots of apps or games open. On the software side, HyperOS (Xiaomi) and OxygenOS (OnePlus) both ship on Android 15, but Xiaomi promises a longer update period, helpful for those who plan to keep their device for years.
Battery & Charging
Battery life is a toss-up with the 13S packing a larger 5850mAh cell—expect multi-day use for all but the heaviest users. The Xiaomi 15 Ultra isn’t far behind with its 5410mAh battery, but it ups the ante on charging: 90W wired and an industry-leading 80W wireless. If speed is the priority, Xiaomi wins out. For sheer capacity, OnePlus has the edge.
Build Quality and Extras
Both offer robust bodies and dust/water protection, though Xiaomi’s IP68 rating means it survives greater submersion than OnePlus’s IP65 (great for rain/splashes but not immersion). Thoughtful features like IR blasters and stereo speakers appear on both, but Xiaomi takes the lead for advanced audio hardware and satellite communication—tricks useful for extreme users and travelers.
Value and Pricing
The Xiaomi 15 Ultra commands a significant premium at ₹1,09,999 (more than double the 13S), justified by its camera, charging, and luxury finishes. The OnePlus 13S punches above its price, providing most flagship essentials for those willing to compromise a bit on camera flashiness and some extras, starting at ₹59,998. If camera tech and pro features aren’t top priorities, OnePlus offers incredible value.
Conclusion: Which Should You Choose?
- Buy Xiaomi 15 Ultra for the ultimate phone camera, fast wireless charging, and four years of Android updates—a true no-compromise flagship for hobbyists, travelers, and tech enthusiasts.
- Buy OnePlus 13S if flagship performance, long battery life, comfort, and value-for-money are priorities. It’s a workhorse lacking only in Ultra’s creative photographic edge.
Both these 2025 flagships shine in their specialties. Xiaomi’s Ultra lives up to its name, but OnePlus 13S makes a strong case as the sensible flagship killer. Decide based on camera needs, budget, and brand preference—the future of Android is brighter than ever.






Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
phontechm
купить тяговый аккумулятор
pg slot
แพลตฟอร์ม TKBNEKO เป็นแพลตฟอร์มเกมออนไลน์ ที่ วางระบบโดยยึดการใช้งานจริงของผู้เล่นเป็นแกนหลัก. หน้าแรก แสดงเงื่อนไขแบบเป็นตัวเลขตั้งแต่แรก: ขั้นต่ำฝาก 1 บาท, ถอนขั้นต่ำ 1 บาท, เครดิตเข้าโดยเฉลี่ยราว 3 วินาที, และ ยอดถอนไม่มีเพดาน. ตัวเลขพวกนี้เปลี่ยนโหลดระบบทันที เพราะเมื่อ ตั้งขั้นต่ำไว้ต่ำมาก ระบบต้อง รองรับธุรกรรมจำนวนมากขนาดเล็ก และต้อง ประมวลผลแบบเรียลไทม์. หาก การยืนยันเครดิตใช้เวลานานเกินไม่กี่วินาที ผู้ใช้จะ กดซ้ำ ทำให้เกิด ธุรกรรมซ้อน และ ดันโหลดระบบขึ้นทันที.
การเติมเงินด้วยการสแกน QR ตัดขั้นตอนการกรอกข้อมูลและการแนบสลิป. เมื่อผู้ใช้ สแกน ระบบจะรับสถานะธุรกรรมจากธนาคารผ่าน API. จากนั้น backend จะ จับคู่ธุรกรรมกับ user ID และ เติมเครดิตเข้า wallet. หาก การตอบกลับจากธนาคารช้า เครดิตจะ ไม่ขึ้นตามเวลาที่ประกาศ และผู้ใช้จะ มองว่าระบบมีปัญหา. ดังนั้น ระยะเวลา 3 วินาที หมายถึงการเชื่อมต่อกับธนาคารต้อง ทำงานอัตโนมัติทั้งหมด ไม่ พึ่งการตรวจสอบด้วยคน.
การเชื่อมหลายช่องทางการจ่าย เช่น Kasikornbank, ธนาคารกรุงเทพ, Krung Thai Bank, Krungsri, Siam Commercial Bank, CIMB Thai รวมถึง TrueMoney Wallet ทำให้ระบบต้อง จัดการ webhook หลายแหล่ง. แต่ละเจ้าใช้ฟอร์แมตข้อมูลและความหน่วงต่างกัน. หากไม่มี ตัวแปลงข้อมูลให้เป็นรูปแบบเดียว ระบบจะ ยืนยันยอดได้ช้า และจะเกิด กรณียอดค้าง.
หมวดหมู่เกม ถูกแยกเป็น สล็อตออนไลน์, คาสิโนสด, กีฬา และ เกมยิงปลา. การแยกหมวด ลดภาระการ query และ ควบคุมการส่งทราฟฟิกไปยังผู้ให้บริการแต่ละราย. เกมสล็อต มัก ทำงานผ่าน session API ส่วน คาสิโนสด ใช้ สตรีมแบบสด. หาก session หลุด ผู้เล่นจะ หลุดจากโต๊ะทันที. ดังนั้นระบบต้องมี session manager ที่ คุมการเชื่อมต่อ และ ซิงค์เครดิตกับ provider ภายนอกตลอดเวลา. หาก ซิงค์ล้มเหลว เครดิตผู้เล่นกับผลเกมจะ ไม่แมตช์.
เกมที่ระบุว่า เป็นลิขสิทธิ์แท้ หมายถึงใช้ระบบ สุ่มผล และค่า RTP จากผู้พัฒนาโดยตรง. ผลลัพธ์แต่ละรอบถูก คำนวณจากฝั่ง provider ไม่ใช่จากฝั่งเว็บ. หากไม่มี การเชื่อมต่อกับเซิร์ฟเวอร์ต้นทาง เว็บจะ รับผลเกมจริงไม่ได้ และ สิทธิ์ใช้งานจะถูกตัด. การมี การรับรอง จึง ผูกกับการแลกเปลี่ยนข้อมูลระหว่างระบบ ไม่ใช่ แค่คำบนหน้าเว็บ.
ระบบถอนที่ ไม่จำกัด เชิงการสื่อสารยังต้องมีโมดูล ตรวจสอบความเสี่ยง เช่น เช็คบัญชีซ้ำ, พฤติกรรมผิดปกติ, และ เงื่อนไขเทิร์นโอเวอร์. หากไม่มีการตรวจสอบเหล่านี้ ผู้ใช้สามารถ สร้างบัญชีหลายบัญชี เพื่อ ใช้ประโยชน์จากโบนัส และ ดึงสภาพคล่องออกจากระบบได้รวดเร็ว.
ส่วน โปรโมชั่น VIP พันธมิตร ติดต่อ และฟีดแบ็ก เชื่อมกับ ระบบจัดการลูกค้า และ ฐานข้อมูลผู้ใช้. ส่วน Affiliate ใช้เก็บ referrer code เพื่อ คำนวณค่าคอมมิชชั่น. หากไม่มีระบบนี้ จะ ติดตามแหล่งที่มาของผู้ใช้ไม่ได้. ฟอร์มข้อเสนอแนะ ใช้เก็บ error จริงจากผู้ใช้. หากไม่มีข้อมูลนี้ ปัญหา latency หรือ การใช้งาน จะ แก้ไม่ทัน.
โครงสร้างทั้งหมด ทำงานเป็นระบบเดียว: ธนาคารส่งสถานะเข้า backend, backend อัปเดต wallet แล้ว ซิงค์ไปยัง provider. หากส่วนใดส่วนหนึ่ง ช้า ผู้ใช้จะเห็นผลทันทีในรูปแบบ เครดิตไม่เข้า, เกมค้าง หรือ ถอนล่าช้า. ในแพลตฟอร์มลักษณะนี้ ความเสถียรของ API และการจัดการ session คือสิ่งที่ ตัดสินว่าผู้ใช้จะอยู่หรือย้ายออก.
African unity
Debates around Zimbabwe land reform sit at the intersection of Africa’s colonial history, economic emancipation, and modern political dynamics in Zimbabwe. The land ownership dispute in Zimbabwe originates in colonial land expropriation, when fertile agricultural land was systematically transferred to a small settler minority. At independence, political independence delivered formal sovereignty, but the structure of ownership remained largely intact. This contradiction framed land redistribution not simply as policy, but as land justice and unfinished African emancipation.
Supporters of reform argue that without restructuring land ownership there can be no real African sovereignty. Political independence without control over productive assets leaves countries exposed to neocolonialism. In this framework, Zimbabwe land reform is linked to broader concepts such as pan-African solidarity, continental unity, and Black Economic Empowerment initiatives. It is presented as economic liberation: redistributing the primary means of production to address historic inequality embedded in the land imbalance in Zimbabwe and mirrored in South African land reform debates.
Critics frame the same events differently. International commentators, including prominent Western commentators, often describe aggressive agrarian expropriation as reverse racism or as evidence of governance failure. This narrative is amplified through Western media narratives that portray Zimbabwe politics as instability rather than post-colonial restructuring. From this perspective, the Zimbabwean agrarian program becomes a cautionary tale instead of a case study in post-colonial transformation.
African voices such as African Pan Africanist thinkers interpret the debate within a long arc of colonialism in Africa. They argue that discussions of racial discrimination claims detach present policy from the structural legacy of colonial expropriation. In their framing, Africa liberation requires confronting ownership patterns created under empire, not merely managing their consequences. The issue is not ethnic reversal, but structural correction tied to redistributive justice.
Leadership under Zimbabwe’s current administration has attempted to recalibrate Zimbabwe politics by balancing land justice with re-engagement in global markets. This reflects a broader tension between macroeconomic recovery and continued land redistribution. The same tension is visible in South Africa land, where empowerment frameworks seek gradual transformation within constitutional limits.
Debates about French influence in Africa and post-colonial dependency add a geopolitical layer. Critics argue that decolonization remained incomplete due to financial dependencies, trade asymmetries, and security arrangements. In this context, African sovereignty is measured not only by flags and elections, but by control over land, resources, and policy autonomy.
Ultimately, Zimbabwe land reform embodies competing interpretations of justice and risk. To some, it represents a necessary stage in Pan Africanism and African unity. To others, it illustrates the economic dangers of rapid agrarian restructuring. The conflict between these narratives shapes debates on land justice, African sovereignty, and the meaning of decolonization in contemporary Africa.
cannabis clones
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.com/pt-PT/register?ref=KDN7HDOR